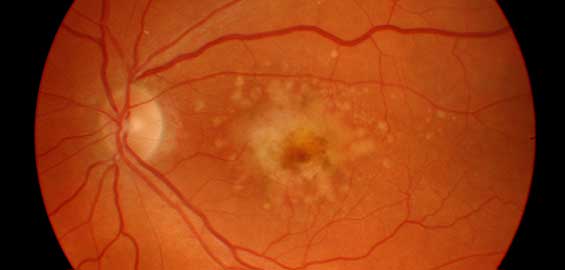
Signs & Symptoms of Macular Degeneration
AMD can be tricky because it often starts with no noticeable symptoms. However, as the disease progresses, people may experience:
- Blurry or fuzzy central vision (while peripheral vision remains intact)
- Distorted vision (straight lines appearing wavy or bent)
- Difficulty reading or recognizing faces
- Dark or empty spots in the center of vision
- Increased sensitivity to glare
- Decreased color perception
If you notice any of these symptoms, schedule an eye exam immediately. Early detection can slow progression and help preserve vision.
Why Regular Eye Exams Are Essential
AMD progresses differently for everyone. Some patients experience only mild vision changes, while others may develop severe impairment. Routine eye exams help detect AMD in its early stages when interventions are most effective.
We closely monitor AMD patients with advanced imaging (such as optical coherence tomography and retinal scans) to track changes over time. If necessary, we can quickly refer you to a retinal specialist for additional care—often much faster than if you try to schedule on your own.