Our Comprehensive Approach to Diabetic Eye Care
At our practice, we take a comprehensive and proactive approach to monitoring and managing diabetic eye health. We understand that diabetes is a lifelong condition that requires careful, ongoing management. Here’s how we help protect your vision:
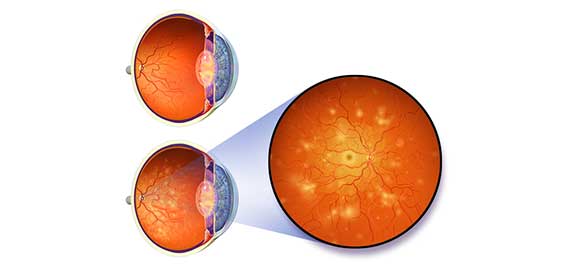
- Baseline Photo-Documentation: The first step in our approach is to establish a clear baseline. We use high-resolution retinal photography to capture detailed images of the back of your eyes. These images provide us with a reference point to monitor any changes over time and are invaluable in detecting subtle shifts in your retinal health before symptoms appear.
- Annual Eye Exams: For most diabetic patients, we recommend an annual comprehensive eye exam, which includes a dilated retinal exam. Dilating the pupils allows us to see the retina more clearly and assess the health of the blood vessels in the eye. If we detect signs of diabetic retinopathy or other diabetic eye diseases, we can intervene earlier to prevent further damage.
- Enhanced Imaging and Monitoring: Depending on the stage of your diabetic eye condition, we may use advanced imaging techniques, such as optical coherence tomography (OCT), to obtain cross-sectional images of the retina. This helps us assess retinal thickness and fluid accumulation, which is important for detecting diabetic macular edema (DME).
- Collaboration with Your Diabetic Care Team: We work closely with your primary care physician, endocrinologist, and other healthcare providers to ensure a comprehensive approach to managing your health. By sharing detailed findings from your eye exam with your diabetic care team, we ensure that your vision is considered in your overall care plan. If any treatments, such as laser therapy, anti-VEGF injections, or corticosteroid injections for DME are needed, we will coordinate with the appropriate specialists.